GENERAL VACUUM TABLE CLAMPING INFORMATION
Ground Principal of Vacuum Clamping
First of all we find the normal atmospheric air pressure inside and outside of the vacuum table, which withholds approximately 1bar. Next some equipment( or work piece) is placed on the vacuum tables surface and the remaining free space and drilled holes are covered with rubber mats. And thus the air in the interior of the vacuum table can be drawn with a vacuum pump. According to the vacuum pump, a pressure difference between the interior and exterior emerges from approximately 100mbar to about 950mbar, and the boundary layer is thus represented by the piece of equipment (or work piece) found on the vacuum table.
As an example, lets say you take a pressure difference of 500mbar. Now depending on the sealing method used with a 200 x 200mm vacuum table the result would be a surface pressure of a maximum 200kp with the equipment or work piece fully covering the whole table surface.
Since one of the most important things in mechanical preparations is to secure the equipment or work piece from slipping or moving out of place, it would make sense that you place a mat or some type of material in between the equipment (work piece) and vacuum plate. Its also good to make sure that this material is airtight and that it also has a high frictional resistance. Depending on the type of vacuum straining, there are various different procedures available here, that can guarantee a optimal solution depending on your specific needs.
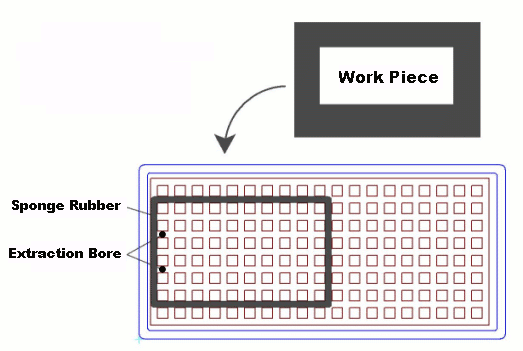
The SQUARE GRID Vacuum Table (SG-Series)
The surface of a Square Grid vacuum table consists solely of armatures, that are connected to a few drilled holes with the vacuum pump. When inserting a moss rubber cord into the armatures one can create a limited boundary around the drilled holes. This limited boundary or field, should correspond the desired workspace. Now the work piece or equipment can be placed and the vacuum can be started.
Advantages:
1. The work piece or equipment does not necessarily need a even underside. With considerable unevenness, approximately one millimeter can be balanced out by the moss rubber cord. For more difficult tasks, rectangular moss rubber cords are also available.
2. Since the work piece (equipment) pushes the moss rubber cord into the armature, its underside lies directly on the aluminum surface of the vacuum table, by what it creates utmost accuracy.
3. Since the system remains sealed during the whole operation, one must not demand so much work to be created from the vacuum pump. Very small outputs of 80-95% of vacuum are sufficient, therefore this procedures becomes very economical.
4. Uniform oscillations and a delay free layer of the whole underside of the work piece (equipment).
Disadvantages:
This procedure can only be used if no openings have to be milled, this is because if its not sealed then this will cause immediate decrease of retention force.
Alternative:
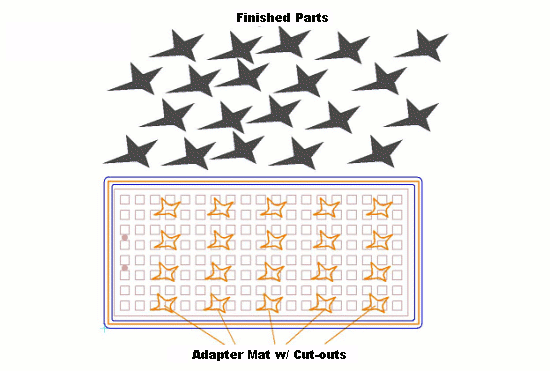
A further possibility to operate a grid (raster) vacuum table is to produce a adapter mat suitable to the respective work piece (equipment). This can be produced out of various materials like e.g : hard rubber, rubber and soft-PVC. The thickness depends on the respective armature gaps and widths. This adapter has openings only where the work piece (equipment) must be held, and is sealed in the places where the milling machine passes through.
Advantages:
1. Openings do not lead to leakage and therefore are no problem.
2. Maximum retention force with minimal demands required for the vacuum pump.
3. The work pieces (equipment) do not require post processing, because they’re whole contour can be worked on using a basic approach all around.
4. No paths must remain standing.
5. The most suitable process in a series (batch) production of smaller parts.
6. Uniform oscillations and a delay free layer of the whole underside of the work piece (equipment).
Disadvantages:
The manufacturing of a adapter mat is just additional expense and effort, that really only amortizes itself in a series (batch) production. Nevertheless the adapter mat can quickly be made with simple means, like for example a scalpel or drilling machine since its not necessary to exactly follow the course of the work piece (equipment) contour.
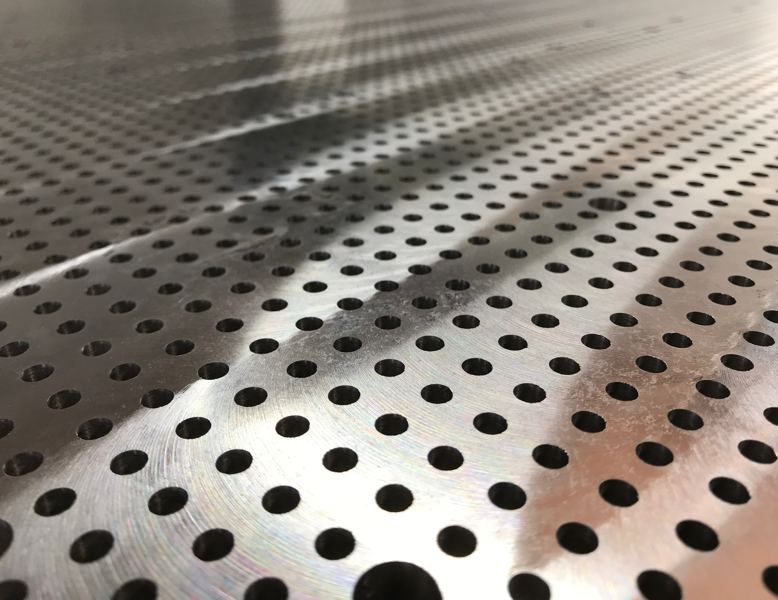
The Hole Grid Vacuum Table (HG-Series)
Here there is a grid out of drilled holes distributed in a relatively narrow distance over the entire surface of the vacuum plate. Sometimes these drilled holes are carried out as a combination between a sack hole with a large diameter and a clearance hole with a relatively small diameter. This has the advantage, that with the help of register pins a proper repositioning work piece (equipment) is possible.
Disadvantageously this technology merely works with the clamping of thin-walled or frail work pieces (equipment), since above the sack holes they dent themselves in the vacuum. For such uses, only vacuum tables with small suction drilled holes can be used. With a hole grid (raster) vacuum table at first its not even attempted to completely seal the table, but one assumes that after placing the work piece (equipment) on the vacuum table and one covers the remaining surface that a certain amount of drilled holes will remain open. The vacuum pump works here with a large volume with a slight differential pressure. This operating principle enables openings during the processing of up to about 15% of the surface. Due to the increase of frictional resistance either a hole rubber mat, where great accuracy is required in the Z-Direction, or a sinter rubber mat as a cheap alternative for the cases where simple cutting is sufficient.
To go without saying a adapter mat can also be using during this process. However, to completely be able to work in the same manner with a grid (raster) vacuum table, a vacuum pump with high differential pressure is required. Should this however also be used for other clamping techniques as by means of a adapter mat in connection with a hole grid (raster) vacuum table, it must as mentioned dispose over a large suction volume. Both together, the high pressure and high volume however place very large demands on the performance of the vacuum pump.
Advantages:
1. Simplest clamping with slight demands on the vacuum pump. First attempts using a simple vacuum generator are very significant.
2. Milling up until a certain point of the entire clamp surface is without a problem doable. This even works with the use of stop pins if a hole rubber mat is used.
3. Full surfaced, sparing and low vibrating work piece (equipment) support.
4. With a series (batch) production using adapter mats to cover free areas is considered economical applicability.
5. Large flexibility is created with register pins with the work pieces (equipments) support.
Disadvantages:
1. Small work pieces (equipment) are only economically workable if these are retained above paths.
2. The vacuum pump has large energy demands (min. 4kw/m²).
3. Slighter retention force by larger leakage than with a square grid vacuum table.